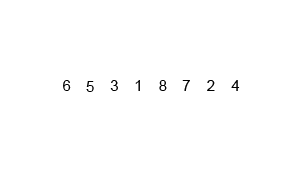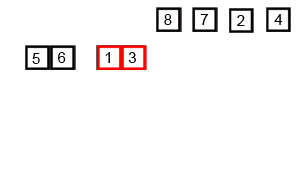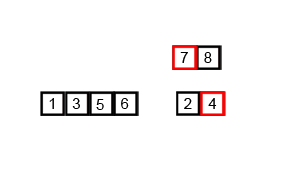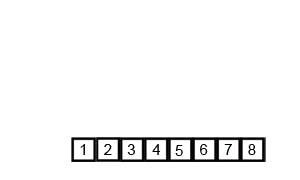 |
| Merge Sort Algorithm |
Merge Sort Algorithm in Data Structure example in Java programming :
public class MergeSort {
private int[] array;
private int[] tempMergArr;
private int length;
public static void main(String a[]) {
int[] inputArr = { 32, 27, 51, 89, 1, 98, 9, 28, 65, 0 };
MergeSort mms = new MergeSort();
mms.sort(inputArr);
for (int i : inputArr) {
System.out.print(i);
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
public void sort(int inputArr[]) {
this.array = inputArr;
this.length = inputArr.length;
this.tempMergArr = new int[length];
doMergeSort(0, length - 1);
}
private void doMergeSort(int lowerIndex, int higherIndex) {
if (lowerIndex < higherIndex) {
int middle = lowerIndex + (higherIndex - lowerIndex) / 2;
// Below step sorts the left side of the array
doMergeSort(lowerIndex, middle);
// Below step sorts the right side of the array
doMergeSort(middle + 1, higherIndex);
// Now merge both sides
mergeParts(lowerIndex, middle, higherIndex);
}
}
private void mergeParts(int lowerIndex, int middle, int higherIndex) {
for (int i = lowerIndex; i <= higherIndex; i++) {
tempMergArr[i] = array[i];
}
int i = lowerIndex;
int j = middle + 1;
int k = lowerIndex;
while (i <= middle && j <= higherIndex) {
if (tempMergArr[i] <= tempMergArr[j]) {
array[k] = tempMergArr[i];
i++;
} else {
array[k] = tempMergArr[j];
j++;
}
k++;
}
while (i <= middle) {
array[k] = tempMergArr[i];
k++;
i++;
}
}
}
OUTPUT
0 1 9 27 28 32 51 65 89 98

0 Comments